ION EXCHANGE SYSTEMS
Pretreatment Equipments
Drinking Water / Mineral Water Plant
Microbiological Treatment Equipments
ENQUIRE NOW
Ion exchange is the reversible exchange of one type of ion present in an insoluble solid with another type of ion with a similar charge present in a surrounding water. Ion exchange is used in chemical purification, substance separation, and water softening or demineralization.
Ion exchange is widely used in the food and beverage industry, hydrometallurgy, metals finishing, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical technology, sugar and sweetener production, ground- and potable-water treatment, nuclear, softening, industrial water treatment, semiconductor, power, and many other industries.
- Ion exchange systems can remove contaminants and improve water quality.
- Ion exchange systems can remove calcium and magnesium, which can make water softer.
The most common ion exchange water treatment methods
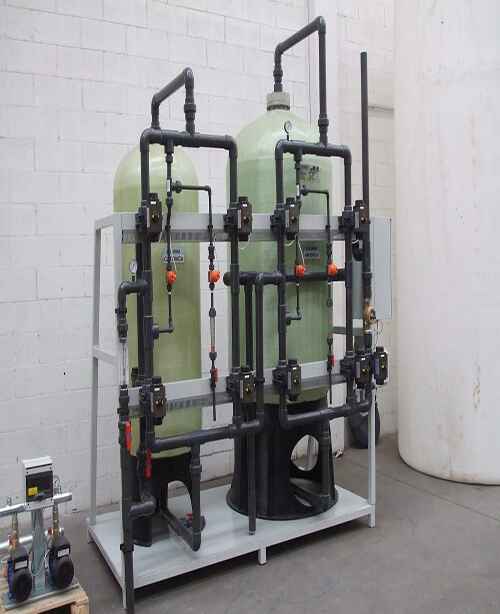
Softner Plant (For Hardness Removal)
Softner plant also known as water softening system is used for the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water . The primary mechanism used for this purpose is a process called ion exchange. APK manufactures softner plant in different sizes and materials manually operated & Fully Automatic.
Raw water contains Calcium and Magnesium which has a scaling tendency in the presence of Alkalinity. The softener unit contains cationic resin in Sodium form. This resin exchanges the calcium and magnesium from water and give out sodium, which does not form scale.
In order to prevent scale retention in boilers, steamers, and other equipment used in the food and beverage processing industry, water softening is essential.
Pharmaceuticals industries used softner plant for various applications like steam generation, equipment cleaning, and element processing. Refineries, power plants, and other industrial facilities depend on softened water to maintain the cooling towers and boilers operating efficiently. Soft water is used by textile manufacturers throughout the dyeing and washing processes to minimize fabric discoloration and improve laundry efficiency.
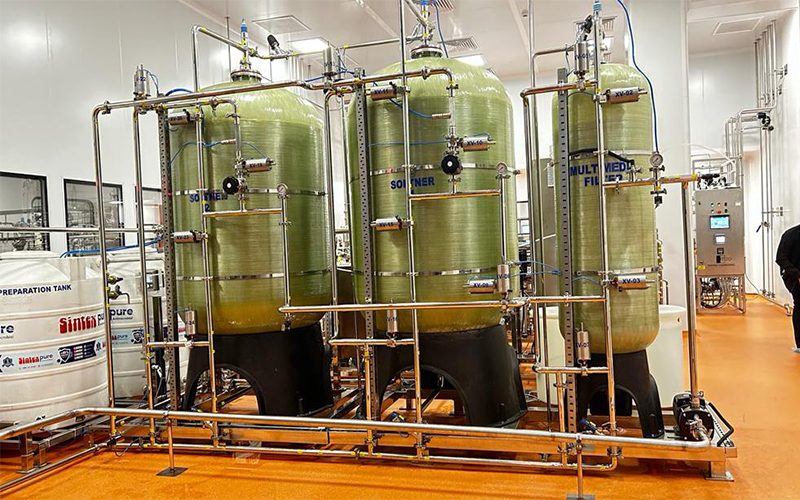

Demineraliser (DM)
APK design DM plant in various sizes & Shapes Manually Operated & Fully Operated as per customer requirement A Demineraliser is a system that removes dissolved ionic chemicals (salts) from water using an ion exchange chemical process. It is sometimes referred to as a Deionized Water System, a Demineraliser, or a DM Plant
The demineralization plants are two-column systems in which the water passes through a cation exchange column first and then an anion. Water contains both positive and negative charged ions. Positive charged ions like calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium etc. called cations. Negative charged ions like chloride, sulfate, carbonate, bicarbonate etc. called anions.
Demineralised water is utilized for different industrial operations because of its high level of quality. Water with a lower purity level might contaminate these processes. When water with a low salt content or insufficient conductivity is required, demineralised water is also utilized.
Demineralised water used for various applications where water conductivity required is low for process for e.g. Beverages, mineral water etc
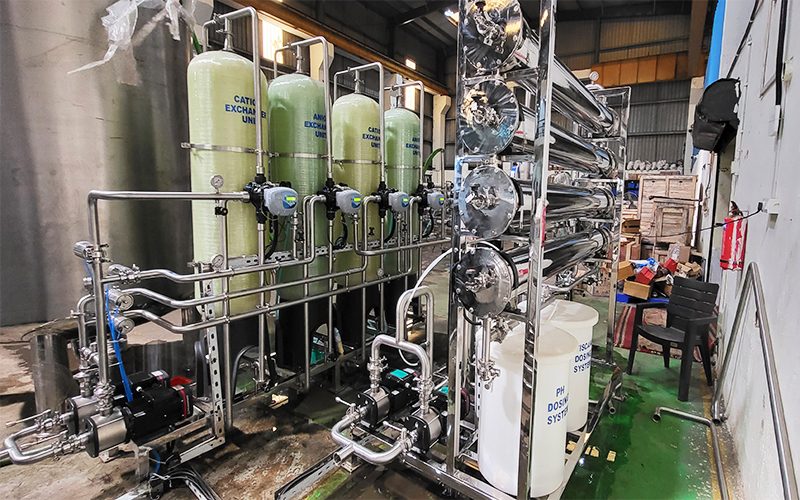

Mixed Bed Ion Exchange - Condensate Polishing Unit:
Mixed bed ion exchange is an ion exchange procedure used to polish demineralised water, remove trace dissolved solids. APK Design & supply Mixed bed to remove traces of soluble inorganic impurities present in the feed water & dissolved ionic contaminants.
A Mixed Bed Ion Exchanger (also known as a Mixed Bed Polisher or a Mixed Bed Filter Or Condensate Polishing Unit) is a vessel that contains both cation exchange resin and anion exchange resin. Mixed bed polishing is an ion exchange-based water treatment technology that comprises of a bed of cation and anion resins, intimately mixed and housed within a cylindrical vessel. The mix of resins provides a perfect environment for the removal of dissolved ionic contaminants. Water runs through this resin mixture during service. Cations dissolved in water are then exchanged for hydrogen ions (H+), whereas anions are exchanged for hydroxide ions (OH-). Water reacts with hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
Mixed Bed Polisher are used to polish water in high-tech industries, such as electronics and medical. And to treat turbine condensate in power stations and process condensate in other industries. Mixed Bed are used to polish sea water distillate.
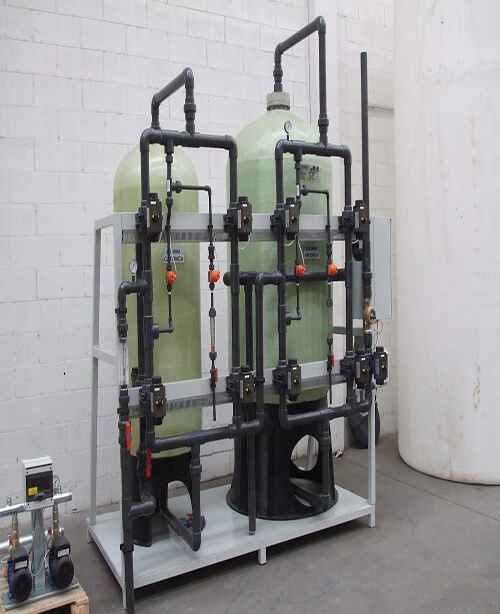

ION EXCHANGE SYSTEMS
Ion exchange is the reversible exchange of one type of ion present in an insoluble solid with another type of ion with a similar charge present in a surrounding water. Ion exchange is used in chemical purification, substance separation, and water softening or demineralization.
Ion exchange is widely used in the food and beverage industry, hydrometallurgy, metals finishing, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical technology, sugar and sweetener production, ground- and potable-water treatment, nuclear, softening, industrial water treatment, semiconductor, power, and many other industries
Ion exchange in Water Treatment System
Ions are a common source of contamination of water. The more ions dissolved in the water, the higher the total dissolved solids (TDS) and conductivity. Ion exchange is the most effective way to rid water of contaminants.
The most common ion exchange water treatment methods are
Softeners
Softner plant also known as water softening system it’s used to the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water.
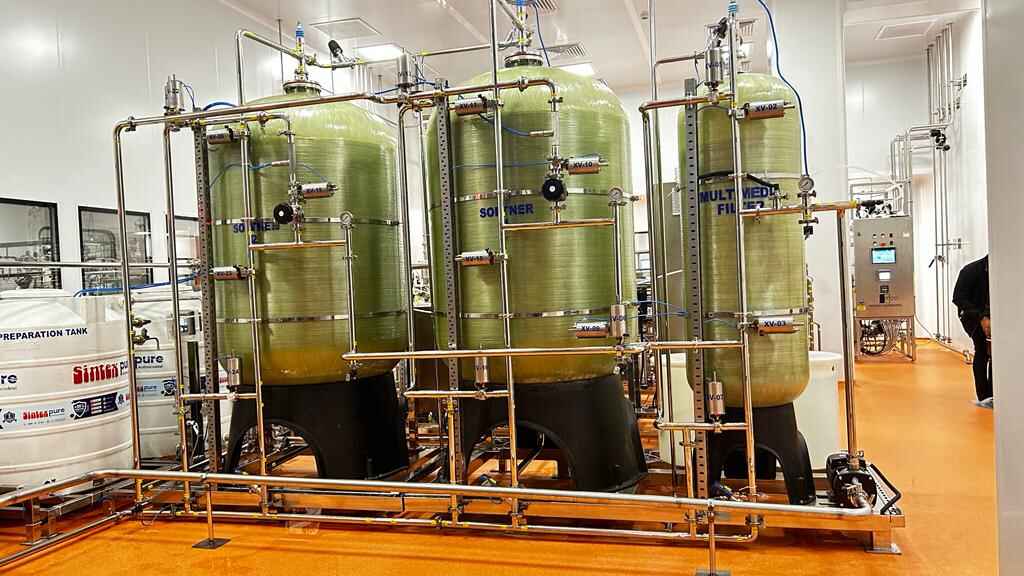
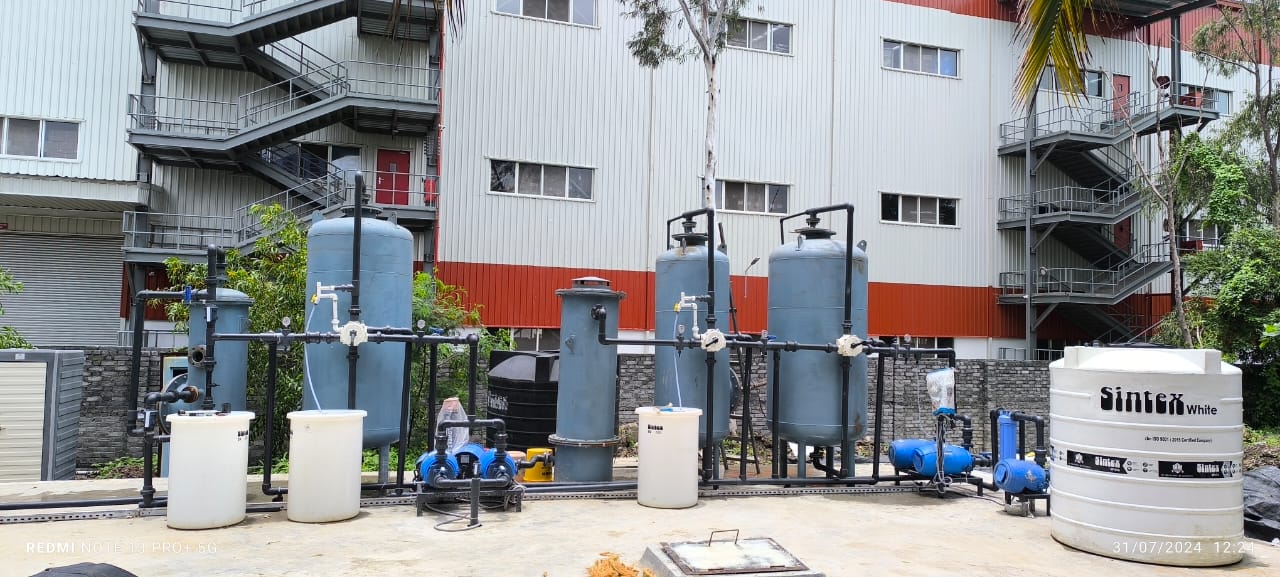


Demineraliser (DM)
A demineraliser is a system that removes dissolved ionic chemicals (salts) from water using an ion exchange chemical process. It is sometimes referred to as a Deionized Water System, a Demineraliser, or a DM Plant
Mixed Bed (MB)
Mixed bed ion exchange is an ion exchange procedure used to polish demineralised water, remove trace dissolved solids.